坦克机器人
此示例项目展示了如何使用 Tank Bot 上的陀螺仪传感器可进行准确转弯。根据您按下的 EV3 积木按钮,机器人会以三角形、正方形、五边形或六边形驱动。
拼搭说明
在本站可查找扩展套装模型的所有拼搭说明。
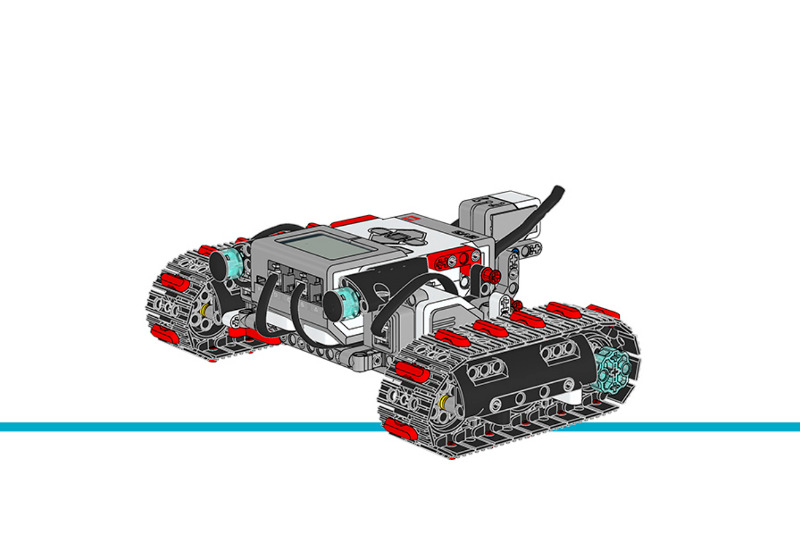
图 33 坦克机器人
示例程序
#!/usr/bin/env pybricks-micropython
"""
Example LEGO® MINDSTORMS® EV3 Tank Bot Program
----------------------------------------------
This program requires LEGO® EV3 MicroPython v2.0.
Download: https://education.lego.com/en-us/support/mindstorms-ev3/python-for-ev3
Building instructions can be found at:
https://education.lego.com/en-us/support/mindstorms-ev3/building-instructions#building-expansion
"""
from pybricks.hubs import EV3Brick
from pybricks.ev3devices import Motor, GyroSensor
from pybricks.parameters import Port, Direction, Button
from pybricks.tools import wait
from pybricks.robotics import DriveBase
from pybricks.media.ev3dev import ImageFile
# Initialize the EV3 brick.
ev3 = EV3Brick()
# Configure 2 motors on Ports B and C. Set the motor directions to
# counterclockwise, so that positive speed values make the robot move
# forward. These will be the left and right motors of the Tank Bot.
left_motor = Motor(Port.B, Direction.COUNTERCLOCKWISE)
right_motor = Motor(Port.C, Direction.COUNTERCLOCKWISE)
# The wheel diameter of the Tank Bot is about 54 mm.
WHEEL_DIAMETER = 54
# The axle track is the distance between the centers of each of the
# wheels. This is about 200 mm for the Tank Bot.
AXLE_TRACK = 200
# The Driving Base is comprised of 2 motors. There is a wheel on each
# motor. The wheel diameter and axle track values are used to make the
# motors move at the correct speed when you give a drive command.
robot = DriveBase(left_motor, right_motor, WHEEL_DIAMETER, AXLE_TRACK)
# Set up the Gyro Sensor. It is used to measure the angle of the robot.
# Keep the Gyro Sensor and EV3 steady when connecting the cable and
# during start-up of the EV3.
gyro_sensor = GyroSensor(Port.S4)
# Initialize the steering and overshoot variables.
steering = 60
overshoot = 5
def right_angle():
# This function drives the robot forward, turn a right angle, drive
# forward again, and then turn 180 degrees to drive back along the
# same path and return to its initial position.
# Reset the Gyro Sensor angle.
gyro_sensor.reset_angle(0)
# Drive forward for 750 millimeters
robot.straight(750)
# Turn clockwise until the angle is 90 degrees.
robot.drive(0, steering)
ev3.speaker.beep()
while gyro_sensor.angle() < 90 - overshoot:
wait(1)
robot.drive(0, 0)
wait(1000)
# Drive forward for 750 millimeters
robot.straight(750)
# Turn clockwise until the angle is 270 degrees.
robot.drive(0, steering)
ev3.speaker.beep()
while gyro_sensor.angle() < 270 - overshoot:
wait(1)
robot.drive(0, 0)
wait(1000)
# Drive forward for 750 millimeters
robot.straight(750)
# Turn counterclockwise until the angle is 180 degrees.
robot.drive(0, -steering)
ev3.speaker.beep()
while gyro_sensor.angle() > 180 + overshoot:
wait(1)
robot.drive(0, 0)
wait(1000)
# Drive forward for 750 millimeters
robot.straight(750)
# Turn clockwise until the angle is 360 degrees.
robot.drive(0, steering)
ev3.speaker.beep()
while gyro_sensor.angle() < 360 - overshoot:
wait(1)
robot.drive(0, 0)
wait(1000)
def polygon(sides, length):
# This function drives the robot along a polygon path. It uses the
# number of sides to calculate the angle to turn to, and the length
# to calculate the time to drive straight.
# Reset the Gyro Sensor angle.
gyro_sensor.reset_angle(0)
# Calculate the angle to turn to and the time to drive straight.
angle = 360 / sides
# Drive along the polygon path.
for side in range(1, sides + 1):
target_angle = side * angle - overshoot
# Drive forward.
robot.straight(length)
# Turn clockwise until the angle equals the target angle.
robot.drive(0, steering)
ev3.speaker.beep()
while gyro_sensor.angle() < target_angle - overshoot:
wait(1)
robot.drive(0, 0)
wait(1000)
# This is the main part of the program. It is a loop that repeats
# endlessly.
#
# First, it waits until any Brick Button is pressed.
# Second, it displays the chosen pattern on the screen.
# Finally, it drives in the chosen pattern.
#
# Then the process starts over, so another pattern can be chosen.
while True:
# Display a question mark to indicate that the robot should await
# instructions.
ev3.screen.load_image(ImageFile.QUESTION_MARK)
# Wait until any Brick Button is pressed.
while not any(ev3.buttons.pressed()):
wait(10)
ev3.screen.clear()
# Respond to the Brick Button press. Display the chosen pattern on
# the screen and drive in this pattern.
if Button.UP in ev3.buttons.pressed():
# Drive in a right angle.
ev3.screen.draw_text(30, 50, "Right Angle")
wait(1000)
right_angle()
if Button.LEFT in ev3.buttons.pressed():
# Drive in a triangle shape.
ev3.screen.draw_text(30, 50, "Triangle")
wait(2000)
polygon(3, 850)
if Button.CENTER in ev3.buttons.pressed():
# Drive in a square shape.
ev3.screen.draw_text(30, 50, "Square")
wait(2000)
polygon(4, 700)
if Button.RIGHT in ev3.buttons.pressed():
# Drive in a pentagon shape.
ev3.screen.draw_text(30, 50, "Pentagon")
wait(2000)
polygon(5, 575)
if Button.DOWN in ev3.buttons.pressed():
# Drive in a hexagon shape.
ev3.screen.draw_text(30, 50, "Hexagon")
wait(2000)
polygon(6, 490)
wait(100) EV3机器人
EV3机器人

